Biophony SoundGarden 2023
Science of Soundbath
Discover what happens when you stimulate your brainwaves through sound and color therapy.
What is a soundbath?
Soundbaths are a type of sound therapy, a healing practice that uses vibrations produced by musical instruments or amplified soundscapes.
This installation will also include chromotherapy, the art of healing through visible color frequencies.
Together, these practices can stimulate the brain to alter your mood through changing frequencies of sound and light.
Brainwave Frequencies
Infra-low (<.5HZ)
Infra-Low brainwaves (also known as Slow Cortical Potentials), are thought to be the basic cortical rhythms that underlie our higher brain functions. Very little is known about infra-low brainwaves. Their slow nature make them difficult to detect and accurately measure, so few studies have been done. They appear to take a major role in brain timing and network function.
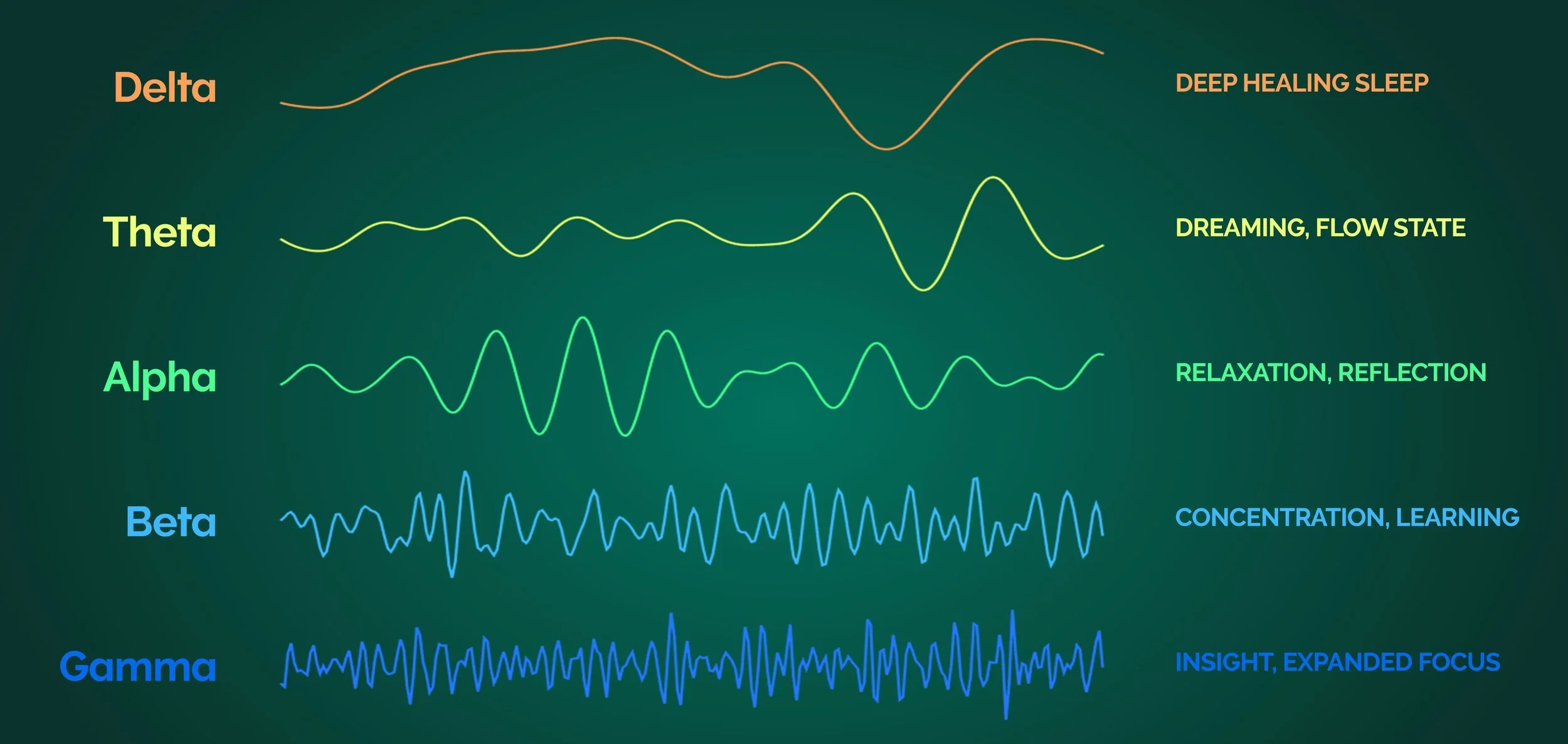
Delta (.5 to 3 Hz)
Delta brainwaves are slow, loud brainwaves (low frequency and deeply penetrating, like a drum beat). They are generated in deepest meditation and dreamless sleep. Delta waves suspend external awareness and are the source of empathy. Healing and regeneration are stimulated in this state, and that is why deep restorative sleep is so essential to the healing process.
Theta (3 to 8 Hz)
Theta brainwaves occur most often in sleep but are also dominant in deep meditation. Theta is our gateway to learning, memory, and intuition. In theta, our senses are withdrawn from the external world and focused on signals originating from within. It is that twilight state which we normally only experience fleetingly as we wake or drift off to sleep. In theta we are in a dream; vivid imagery, intuition and information beyond our normal conscious awareness. It’s where we hold our ‘stuff’, our fears, troubled history, and nightmares.
Alpha (8 to 12 Hz)
Alpha brainwaves are dominant during quietly flowing thoughts, and in some meditative states. Alpha is ‘the power of now’, being here, in the present. Alpha is the resting state for the brain. Alpha waves aid overall mental coordination, calmness, alertness, mind/body integration and learning.
Beta (12 to 38 Hz)
Beta brainwaves dominate our normal waking state of consciousness when attention is directed towards cognitive tasks and the outside world. Beta is a ‘fast’ activity, present when we are alert, attentive, engaged in problem solving, judgment, decision making, or focused mental activity.
Beta brainwaves are further divided into three bands; Lo-Beta (Beta1, 12-15Hz) can be thought of as a 'fast idle', or musing. Beta (Beta2, 15-22Hz) is high engagement or actively figuring something out. Hi-Beta (Beta3, 22-38Hz) is highly complex thought, integrating new experiences, high anxiety, or excitement. Continual high frequency processing is not a very efficient way to run the brain, as it takes a tremendous amount of energy.
Gamma (38 to 42 Hz)
Gamma brainwaves are the fastest of brain waves (high frequency, like a flute), and relate to simultaneous processing of information from different brain areas. Gamma brainwaves pass information rapidly and quietly. The most subtle of the brainwave frequencies, the mind has to be quiet to access gamma.
Brainwave Entrainment
Brainwave entrainment is a method to stimulate the brain into entering a specific state by using a pulsing sound, light, or electromagnetic field. The pulses elicit the brain’s ‘frequency following’ response, encouraging the brainwaves to align to the frequency of a given beat.
This ‘frequency following’ response of brainwave entrainment can be seen in action with those prone to epilepsy. If a strobe flashes at their seizure frequency, the brain will ‘entrain’ to the flashing light, resulting in a seizure.
On the positive side, this same mechanism is commonly used to induce many brainwave states; such as a trance, enhanced focus, relaxation, meditation or sleep induction. The brainwave entrainment effectively pushes the entire brain into a certain state.
Brainwave entrainment works for almost everyone. It is a great way to lead your mind into states that you might usually have difficulty reaching, allowing you to experience what those states feel like.
At the root of all our thoughts, emotions and behaviors are the communication between neurons within our brains. Brainwaves are produced by synchronized electrical pulses from masses of neurons communicating with each other. Brainwaves are detected using sensors placed on the scalp. They are divided into bandwidths to describe their functions, but are best thought of as a continuous spectrum of consciousness; from slow, loud and functional - to fast, subtle, and complex.
It is a handy analogy to think of brainwaves as musical notes - the low frequency waves are like a deeply penetrating drum beat, while the higher frequency brainwaves are more like a subtle high pitched flute. Like a symphony, the higher and lower frequencies link and cohere with each other through harmonics.
Our brainwaves change according to what we’re doing and feeling. When slower brainwaves are dominant we can feel tired, slow, sluggish, or dreamy. The higher frequencies are dominant when we feel wired, or hyper-alert.
The descriptions that follow are only broad descriptions - in practice things are far more complex, and brainwaves reflect different aspects when they occur in different locations in the brain.
Binaural Beats
A binaural beat is an auditory illusion perceived when two different pure-tone sine waves, both with frequencies lower than 1500 Hz, with less than a 40 Hz difference between them, are presented to a listener dichotically (one through each ear).
For example, if a 440 Hz pure tone is presented to a subject's right ear, while a 430 Hz pure tone is presented to the subject's left ear, the listener will perceive the auditory illusion of a pulsating tone, in addition to the two pure-tones presented to each ear. The third sound is called a binaural beat, and in this example would have a perceived pitch correlating to a frequency of 10 Hz, that being the difference between the 440 Hz and 430 Hz pure tones presented to each ear.
Binaural-beat perception originates in the inferior colliculus of the midbrain and the superior olivary complex of the brainstem, where auditory signals from each ear are integrated and precipitate electrical impulses along neural pathways through the reticular formation up the midbrain to the thalamus, auditory cortex, and other cortical regions.